By Hong Soon-do, Beijing correspondent, AsiaToday - The smog season is coming soon as Beijing and other north-central metropolis in China will activate their winter heating system on November 15. As a result, it's clear that Korea will have to breathe bad air over the next few months.
According to Beijing's meteorological officials on Thursday, such outlook is closely related to the fact that most cities in China heavily rely on coal as a fuel for winter heating. Coal accounts for nearly 70% of total heating fuel used in Beijing. China's three Northeastern Provinces, where their economy is relatively undeveloped, rely on coal even more. Harbin, the capital of Heilongjiang province, relies on coal over 80%. The level of fine particulate matter, or PM2.5, in Harbin's air is often 10 times higher than the international safety standard (25).
Moreover, there are car fuels are that are problematic in terms of quality, and old factories, which are one of the major sources of pollution in China. Besides yellow dust often occurs in winter. In short, China could face worst pollution with winter ahead.
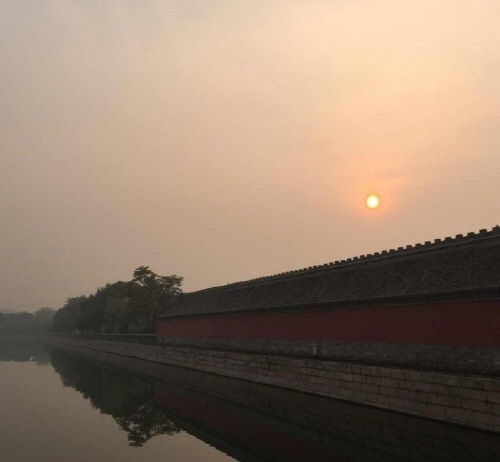 It's smog season in China. The smoggy view of Tiananmen on Thursday shows the current situation in China./ Source from search engine Baidu It's smog season in China. The smoggy view of Tiananmen on Thursday shows the current situation in China./ Source from search engine Baidu |
This outlook is not an exaggeration to say considering the fact that smog hit Beijing for four days from Nov. 2 to 5. The PM2.5 levels in Beijing's air reached close to 300 on Thursday morning and the city lifted its smog alert level from blue to yellow. But Yet, it's highly likely that things will get worse when winter heating starts on November 15.
It seems dust and smog is an inevitable fate that Korea faces as westerly winds carry the smog from China to the Korean peninsula. It is highly likely considering the fact that yellow dust from Gobi Desert can fly to Amazon in Brazil.
Of course, the air quality in Beijing and northern China has improved. In Beijing, the levels of PM2.5 particles dropped by 21.8% compared to last year. However, the average cumulative concentrations of PM2.5 stands at nearly 70 micrograms per cubic meter, which is three times higher than international standards. It means that China as well as Korea will suffer from severe smog for a while.
Most Read
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7